
BLOGS
Keyword Research
Understanding Keywords and Their Role in SEO
A keyword is a term or phrase that people usually type in the search bar of a search engine to find something they want.
In the realm of SEO and online content, keywords play a crucial role in helping users and search engines find and understand the content on webpages. They are used to optimize content for search engine visibility, enabling people to discover relevant information by entering these keywords into search engines.
In our guide, you can learn:
- Why are keywords so important for SEO
- How to Gain Visibility on Google for Targeted Keywords
- How to find keywords for SEO
- Key Factors for Choosing a Keyword
- Where to Put Your Keywords for Optimization
- What are Long Tail Keywords?
- What Are The Supporting Long Tail Keywords?
- About Topical Long Tail Keywords
Why are keywords so important for SEO?
Keywords are of paramount importance in the field of SEO (Search Engine Optimization) because they are the foundation of how search engines understand and rank web content. By using relevant keywords strategically, website owners can significantly improve their online visibility and attract more organic traffic.
Here’s an example to illustrate this:
Imagine you have a website that sells custom-made artisanal chocolates. If someone is searching for “handcrafted chocolate gifts” on a search engine, and your website is optimized with this specific keyword, it’s more likely to appear in the search results. If your content effectively incorporates keywords related to your products and services, your website will be more visible to potential customers.
In this way, keywords serve as a bridge between what users are searching for and what your website offers. They enable search engines to match user queries with relevant content, ultimately driving more visitors to your site, which can lead to increased sales or engagement. Therefore, choosing and using the right keywords is a fundamental aspect of SEO success.
How to Gain Visibility on Google for Targeted Keywords
There are two ways mainly to gain visibility on Google by that you will get lots of traffic. They are:
- PPC (Pay Per Click) Ads
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
Pay Per Click- Advertisement
“Pay Per Click Advertisement” is an online advertising model where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked by a user.
This model is commonly used in search engine advertising. It allows advertisers to bid on specific keywords or target audiences, and they only incur costs when a user interacts with their ad by clicking on it.
PPC is an effective way to drive targeted traffic to websites and is often used to achieve various marketing goals, such as lead generation, e-commerce sales, or brand awareness.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing a website or online content to improve its visibility in search engine results. The goal is to rank higher for specific keywords and phrases that are relevant to the content, ultimately attracting more organic (non-paid) traffic.
For example, if you have a website that sells fitness equipment, you’d want to optimize it for keywords like “home gym equipment” or “best workout gear.” By strategically using these keywords in your content, meta tags, and other on-page elements, your website is more likely to appear on the first page of search results when someone searches for those terms.
As a result, you can attract users interested in fitness equipment, potentially leading to more sales and website traffic. SEO is essential for businesses and website owners to enhance their online presence and reach their target audience effectively.
How to find keywords for SEO
To find keywords for SEO, you can use various tools and techniques to identify relevant terms and phrases that potential visitors might use when searching for your content or products. Here’s a real example:
Suppose you run a website selling organic skincare products. You can start your keyword research by using tools like Google’s Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush. Enter broad terms like “organic skincare,” and these tools will generate a list of related keywords and phrases.
From the results, you might discover keywords like “natural anti-aging creams,” “best organic face serums,” or “chemical-free skincare routine.” These are specific terms that your target audience is likely searching for. You can then incorporate these keywords naturally into your website content, meta tags, and blog posts to improve your site’s visibility in search results. This way, you’ll attract visitors interested in organic skincare products and potentially boost your online sales.
Key Factors for Choosing a Keyword
When choosing keywords, consider four key factors:
- Relevance
- Search Volume
- Competition
- User Intent
Relevance
The role of relevance in choosing keywords for SEO cannot be overstated. Relevance ensures that the keywords you target align closely with the content, products, or services you offer, thereby attracting the right audience to your website.
For instance, if you run an online shoe store specializing in athletic footwear, targeting keywords like “running shoes,” “athletic sneakers,” or “cross-training shoes” is highly relevant. This relevance helps your website appear in search results when users are actively seeking the products you provide.
By focusing on relevant keywords, you not only increase the likelihood of attracting potential customers but also improve the overall user experience, as visitors find the information or products they are looking for, leading to higher engagement and conversions.
Search Volume
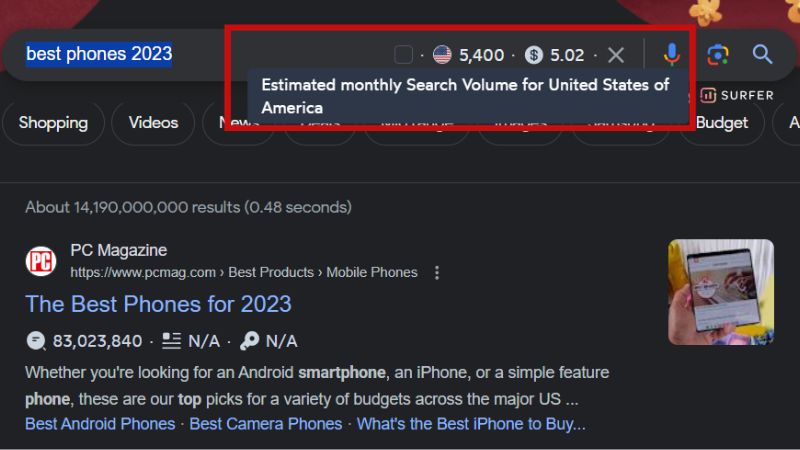
The importance of search volume in choosing keywords for SEO is crucial for understanding the potential reach and visibility of your content or website.
Search volume represents how often a specific keyword or phrase is entered into search engines within a given time frame. For example, if you operate a tech blog and are considering two keywords, “smartphone reviews” and “best phones 2024,” you might discover that “smartphone reviews” has a significantly higher search volume.
This data indicates that more users are searching for general smartphone reviews. By targeting keywords with substantial search volume, you can tap into a larger audience and potentially generate more organic traffic to your website. However, it’s essential to strike a balance between search volume and competition to find the sweet spot for your SEO strategy.
Competition
Keyword competition indicates how many other websites are targeting the same keywords. While high-competition keywords may offer significant traffic potential, they can be challenging to rank for, especially for newer websites.
On the other hand, low-competition keywords are easier to rank for but may have lower search volumes. Striking the right balance is essential. By incorporating a mix of high- and low-competition keywords, you can attract both immediate traffic and build a foundation for future growth.
For instance, if you’re in the field of tech accessories, targeting highly competitive terms like “smartphone cases” may be tough, but focusing on less competitive keywords like “custom iPhone 13 case designs” could offer an opportunity to establish your presence and gradually compete in the broader market.
User Intent
User intent plays a pivotal role in the selection of keywords for SEO. Understanding what users are looking to accomplish with their search queries is crucial in delivering relevant content.
If a user types “best hiking trails in California,” their intent is likely informational, seeking insights on where to hike. On the other hand, if someone searches for “buy camping gear online,” their intent is transactional, indicating they are ready to make a purchase.
By discerning user intent and tailoring keywords accordingly, you can create content and optimize your website to cater to users’ specific needs. This not only improves the chances of your site appearing in search results but also enhances the user experience by providing the most pertinent information or services, increasing the likelihood of conversions and customer satisfaction.
Where to Put Your Keywords for Optimization
To optimize your keywords effectively, strategically place them in key areas of your website and content.
Incorporate keywords naturally within your content’s body, headings, and subheadings, ensuring they flow seamlessly to provide value to the reader. Utilize keywords in meta tags, such as the meta title and meta description, as these elements impact your website’s appearance in search engine results.
Include keywords in your URL structure to create a logical and descriptive web address. Additionally, use keywords in alt tags for images to improve accessibility and SEO. Remember that while keyword optimization is crucial, it should always serve the primary goal of delivering a great user experience and valuable content.
Striking the right balance between keyword placement and high-quality, informative content is key to attracting both search engines and human visitors, leading to improved search engine rankings and increased organic traffic.
What are Long Tail Keywords?
Long-tail keywords are specific and often longer phrases that users enter into search engines when looking for very particular information, products, or services. These keywords are more detailed and less generic than short-tail or broad keywords, and they typically have lower search volumes but higher relevance to a specific topic or audience.
For example, a short-tail keyword could be “shoes,” whereas a long-tail keyword might be “women’s running shoes with arch support.” Long-tail keywords allow businesses to target a niche audience and answer specific user queries, making them valuable for SEO and content strategies.
While they may not bring as much traffic as broader keywords, long-tail keywords often result in higher conversion rates because they attract users who are closer to making a decision or purchase due to their precise search intent.
What Are The Supporting Long Tail Keywords?
Supporting long-tail keywords are specific keyword phrases that complement your primary or main long-tail keyword, often addressing related subtopics or aspects of a broader subject. They are used to create a more comprehensive and detailed content strategy.
For example, if your main long-tail keyword is “best digital cameras for travel photography,” supporting long-tail keywords could include phrases like “compact mirrorless camera options,” “camera gear for landscape shots,” or “travel photography tips for beginners.” These supporting long-tail keywords allow you to create in-depth content that covers different aspects of the main topic, providing valuable information to a broader audience and improving your website’s chances of ranking well in search engine results for a variety of related queries.
By incorporating supporting long-tail keywords into your content, you can enhance the depth and relevance of your material, catering to a wider range of search queries and user interests while improving your overall SEO strategy.
Let’s Know About Topical Long Tail Keywords
Topical long-tail keywords are specific keyword phrases that dive into distinct subtopics or aspects within a broader subject area. These keywords are essential for content creators and SEO strategists looking to cater to a more specialized or diverse audience.
By focusing on topical long-tail keywords, you can develop content that delves deeper into particular areas of interest, making your website a valuable resource for a wide range of queries and user needs.
For example, in the field of “digital marketing,” you might use the topical long-tail keyword “content marketing strategies for startups.” This phrase narrows down the broader topic of digital marketing to a specific subtopic: content marketing for startup businesses. By addressing this subtopic with dedicated content, you not only attract a more targeted audience but also establish your website as a credible source for in-depth information within your niche.
Topical long-tail keywords help you provide more comprehensive and relevant content to your audience, enhancing your site’s overall visibility and authority in your chosen field. They are an invaluable component of a robust SEO strategy and content marketing plan.
Keywords are the fundamental building blocks of a successful SEO strategy. They are the language that connects your content to search engine users, helping you reach the right audience and improve your online visibility. As we’ve explored in this blog, choosing the right keywords and strategically placing them within your content, meta tags, and on-page elements is a crucial step in optimizing your website for search engines.
It’s important to remember that SEO is a dynamic field, and keyword strategies must adapt to changing user behaviors and search engine algorithms. Keeping your finger on the pulse of your industry and regularly refining your keyword research and optimization techniques is key to staying competitive in the digital landscape.
Long-Tail Keywords: The Secret to Getting More Search Traffic
This guide explains the importance of long-tail keywords in SEO. It discusses how these specific search phrases, which have less competition, can bring targeted traffic to your website.
By using long-tail keywords effectively, you can optimize your content and attract a valuable audience. This will ultimately increase your search traffic and enhance your online presence.
By this guide you will know about:
- About Long-tail Keywords
- Why Are Long-Tail Keywords Considered Great?
- How to discover long-tail keywords
- Types of Long-tail Keywords
About Long-tail Keywords
What are they?
Long-tail keywords are highly specific and longer search phrases that users enter into search engines when they’re looking for very particular information or solutions. They typically consist of three or more words and tend to be less competitive than shorter, more generic keywords. Here’s a real example to illustrate long-tail keywords:
Short Keyword: “Shoes”
Long-Tail Keyword: “Women’s vegan leather hiking boots for winter”
In this example, “Shoes” is a broad, generic keyword that could refer to various types of footwear. On the other hand, “Women’s vegan leather hiking boots for winter” is a long-tail keyword, offering a very precise description of the product the user is interested in.
Long-tail keywords are beneficial for both searchers and content creators. Users find more relevant results, while website owners can target niche audiences and improve their chances of ranking higher in search engine results for these specific queries.
What is the reason behind the name “long-tail” keywords?
The term “long-tail” keywords in the context of SEO originates from the shape of the demand curve in a sales distribution graph.
The curve typically shows that a few highly popular, or “head,” keywords drive the majority of search traffic, while a vast number of less popular, specific, and longer phrases, known as “long-tail” keywords, collectively make up the tail end of the distribution.
Here’s an example to illustrate this concept:
Imagine you run an online bookstore. “Books” would be a head keyword, as it’s broad and highly competitive. However, the demand curve extends into the long tail with specific, less competitive phrases, like:
- “Mystery novels set in Victorian London”
- “Best gluten-free cookbooks for beginners”
- “Science fiction books with time travel themes”
These long-tail keywords are more specific and target a narrower audience. While they may individually receive less search traffic, when you add them up, they often surpass the traffic generated by the more generic head keyword “Books.”
Hence, the name “long-tail” keywords because they represent the extended tail end of the demand distribution, which collectively can be highly valuable for attracting niche, interested users to your website.
Why Are Long-Tail Keywords Considered Great?
Long-tail keywords are considered great for SEO and content strategy for several reasons, each of which provides a unique advantage. Here are key reasons with real examples:
Targeted audience
Long-tail keywords allow you to reach a highly targeted audience interested in specific topics or products. For instance, if you run a website selling hiking gear, the long-tail keyword “best waterproof hiking boots for women” caters to an audience seeking precisely that product.
By optimizing your content around such keywords, you attract users with a clear intent to make a purchase or gather detailed information.
Lower competition
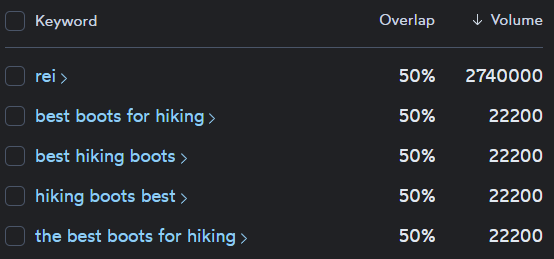
Long-tail keywords are often less competitive than broad, generic terms. This reduces the difficulty of ranking well in search results. For example, “hiking boots” is highly competitive, but “best waterproof hiking boots for women” has less competition, making it easier for your content to appear on the first page of search results.
Higher conversion rates
Due to their specificity, long-tail keywords tend to yield higher conversion rates. When users find content that precisely matches their search intent, they are more likely to engage, whether by making a purchase or subscribing to your newsletter.
Consider the long-tail keyword “organic vegetarian restaurants in San Francisco.” Users searching for this are more likely to dine out at one of the suggested restaurants.
By leveraging long-tail keywords like these, you can tap into valuable niche markets, attract motivated visitors, and increase your chances of conversion, making them an essential component of an effective SEO and content strategy.
How to discover long-tail keywords
Discovering long-tail keywords is a crucial aspect of SEO and content strategy. Here are five methods to uncover long-tail keywords, each with a real example to illustrate:
Keyword Research Tools
Utilize keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to find long-tail keywords related to your niche. For instance, if you have a tech blog, you might discover “best budget laptops for video editing” as a relevant long-tail keyword with decent search volume.
Google Suggest
Start typing a broad term into Google’s search bar, and it will suggest related search queries. For example, entering “digital marketing” could prompt suggestions like “digital marketing strategies for small businesses,” which is a long-tail keyword.
Google’s “People Also Ask”
When you search for a topic on Google, you’ll often find a “People Also Ask” section. These questions are great sources of long-tail keywords. For instance, if you search for “home gardening,” you might see “How to grow tomatoes in small spaces,” which can be a long-tail keyword.
Competitor Analysis
Analyze your competitors’ content and meta tags to identify long-tail keywords they are targeting. For a fitness blog, your competitor might be optimizing for “effective HIIT workouts for beginners.”
User-generated Content
Forums, social media, and community platforms like Reddit can be treasure troves of long-tail keywords. If you find discussions about “overcoming jet lag while traveling,” you’ve identified a long-tail keyword relevant to travel content.
By employing these methods, you can uncover a wealth of long-tail keywords that align with your content’s focus and meet the specific needs of your target audience. These keywords can serve as the foundation for creating highly targeted and engaging content that ranks well in search results.
Types of Long-tail Keywords
Two common types of long-tail keywords are:
1. Product-specific long-tail keywords
Example: “Sony PlayStation 5 price in USA”
These keywords are highly specific and often include product names, brands, and location details. They cater to users looking for particular products or services and are close to making a purchase decision. In this example, the user is likely interested in purchasing a Sony PlayStation 5 in the USA and wants to know the price.
2. Question-Based Long-Tail Keywords
Example: “How to bake a gluten-free chocolate cake”
Question-based long-tail keywords often begin with interrogative words like “how,” “what,” “why,” “where,” and “when.” They address users seeking answers, information, or solutions to specific queries. In this case, the user is looking for instructions on baking a gluten-free chocolate cake, indicating a specific informational need.
These types of long-tail keywords cater to different user intents, whether it’s making a purchase, seeking information, or finding solutions.
Incorporating both product-specific and question-based long-tail keywords in your content strategy can help you capture a broad range of user needs and improve your content’s visibility in search results.
Long-tail keywords are a powerful tool for increasing search traffic. These specific phrases connect you with a targeted audience, improve your content’s relevance, and enhance your SEO strategy.
By understanding and using long-tail keywords effectively, you can improve search rankings and attract engaged visitors who are more likely to convert. Quality content and strategic use of long-tail keywords are the key to success in online search.
Branded Search and Non-Branded Search: What You Need to Know
Understanding the differences between branded and non-branded search is essential in the complex realm of search engine optimization (SEO). These two aspects have distinct impacts on online visibility, user experience, and overall digital strategy. In this analysis, we explore the intricacies of branded and non-branded search, offering valuable insights to help you develop a strong SEO strategy.
Defining Branded and Non-Branded Search
Branded Search:
Branded search refers to online queries explicitly tied to a brand or company. These searches typically include the brand name or variations of it. For instance, a user searching for “Nike shoes” or “Apple iPhone” is engaging in branded search. Branded searches are a direct reflection of a user’s awareness of a specific brand and their intention to find information or products related to that brand.
Non-Branded Search:
On the other hand, non-branded search encompasses queries that are not tied to a specific brand. Users conducting non-branded searches are seeking general information or solutions without specifying a particular brand. For example, a user searching for “running shoes for beginners” or “smartphones with high-quality cameras” is engaging in non-branded search. Non-branded searches are more exploratory and often indicate a user’s broader interests or needs.
Key Distinctions Between Branded and Non-Branded Search:
1. User Intent:
- Branded Search: Users conducting branded searches typically have a specific brand or product in mind. Their intent is often transactional, aiming to access the official website, make a purchase, or gather detailed information about the brand.
- Non-Branded Search: Users engaging in non-branded searches may be in the early stages of their buyer’s journey. Their intent is often informational, looking for reviews, comparisons, or general insights rather than being tied to a particular brand.
2. Competition:
- Branded Search: The competition in branded search is usually lower since users are explicitly searching for a specific brand. However, competitors may target your brand terms, emphasizing the need for a strong online presence.
- Non-Branded Search: Competition for non-branded terms can be fierce, as multiple brands may vie for visibility. Success in non-branded search often requires a comprehensive SEO strategy and a focus on content relevance.
3. Brand Authority:
- Branded Search: A strong brand presence and positive brand reputation are crucial in branded search. Users expect to find authoritative information, official sources, and a seamless brand experience.
- Non-Branded Search: Establishing brand authority in non-branded search involves creating high-quality, informative content. Brands that consistently provide valuable information become trusted resources in their industry.
Navigating the SEO Strategy:
1. Optimize for Branded Search:
- Claim Your Brand Space: Ensure that your official website ranks prominently for branded searches. Claim your Google My Business listing, optimize meta tags, and maintain accurate business information to enhance visibility.
- Protect Against Competitors: Monitor and address attempts by competitors to bid on your brand terms in paid search. Consistently deliver exceptional products and services to reinforce customer loyalty.
2. Excel in Non-Branded Search:
- Keyword Research: Conduct thorough keyword research to identify relevant non-branded terms related to your industry, products, or services. Optimize your content to align with these keywords and user intent.
- Content is Key: Develop high-quality, informative content that addresses the needs and questions of your target audience. Blog posts, guides, and tutorials can position your brand as an authority in your field.
3. Bridge the Gap:
- Unified Messaging: Ensure consistency in your messaging across both branded and non-branded content. Create a unified brand narrative that reinforces your value proposition, regardless of how users discover your brand.
- User Experience Matters: Whether users arrive through a branded or non-branded search, prioritize a seamless user experience. A well-designed website, easy navigation, and clear calls-to-action contribute to positive user interactions.
Measuring Success:
1. Branded Search Metrics:
- Direct Traffic: Monitor direct traffic to your website, as this often includes users who have specifically searched for your brand. An increase in direct traffic can indicate growing brand awareness.
- Brand Impressions: Utilize tools like Google Search Console to track impressions and clicks for branded queries. Analyze trends over time to gauge the effectiveness of your branded search optimization efforts.
2. Non-Branded Search Metrics:
- Keyword Rankings: Track your rankings for non-branded keywords relevant to your industry. Regularly assess your position in search engine results pages (SERPs) to identify areas for improvement.
- Organic Traffic: Measure the organic traffic to your site, focusing on sources that stem from non-branded searches. An upward trend in organic traffic indicates improved visibility for generic industry-related queries.
A Holistic Approach to SEO
Understanding the intricacies of both branded and non-branded search is fundamental to developing a holistic SEO strategy. Balancing optimization for brand-specific queries and broader industry-related searches enables brands to capture a diverse audience and foster long-term success. As search engine algorithms evolve, maintaining agility in your SEO strategy, adapting to user behavior, and consistently delivering value will be the key to sustained online visibility and success.
The 10 Most Important Types of Keywords
In the intricate dance of search engine optimization (SEO), keywords are the compass guiding users to your digital doorstep. Understanding the nuances of different keyword types is crucial for unlocking the full potential of your SEO strategy. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore 10 actionable ways to navigate the SEO landscape and craft keywords that not only boost your website’s authority but also stand the test of time.
1. Short-Tail Keywords: Unlocking Broad Reach
Short-tail keywords, often referred to as “head” keywords, are brief and general terms consisting of one or two words. While these keywords boast high search volumes, they are also highly competitive. Examples include “shoes” or “digital marketing.” Incorporating short-tail keywords strategically in your content broadens your reach but requires a robust SEO strategy to stand out in the crowd.
2. Long-Tail Keywords: Niche Precision for Targeted Traffic
Contrary to short-tail keywords, long-tail keywords consist of three or more words and are more specific. Examples include “best running shoes for flat feet” or “digital marketing tips for small businesses.” While long-tail keywords may have lower search volumes, they attract highly targeted traffic, enhancing the likelihood of conversion. Integrating long-tail keywords into your content provides a nuanced approach to capturing specific audience needs.
3. Transactional Keywords: Driving Conversions
Transactional keywords signal an intent to make a purchase or take a specific action. Examples include “buy smartphones online” or “sign up for a digital marketing course.” Incorporating transactional keywords strategically in product pages or call-to-action sections can boost conversions by aligning with user intent.
4. Informational Keywords: Educating and Building Authority
Informational keywords cater to users seeking knowledge or answers. Examples include “how to tie a tie” or “history of digital marketing.” Creating content that addresses informational queries establishes your website as an authoritative source in your niche, building trust and potentially attracting backlinks.
5. Navigational Keywords: Guiding Users to Specific Content
Navigational keywords help users find a particular website or page. Examples include “Facebook login” or “Nike official website.” While these keywords are often brand-specific, optimizing your content for navigational queries ensures users can easily locate the information or products they seek on your site.
6. Branded Keywords: Strengthening Your Digital Identity
Branded keywords include your business or product name. Examples include “Nike shoes” or “Apple iPhone.” Optimizing for branded keywords is essential for strengthening your digital identity, enhancing brand recognition, and ensuring your audience can find you when specifically searching for your brand.
7. Competitor Keywords: Capitalizing on Industry Presence
Targeting competitor keywords involves optimizing your content to appear in search results when users search for your competitors. For example, if you’re a coffee shop, optimizing for “Starbucks alternatives” can attract users exploring alternatives. While not a primary strategy, judiciously incorporating competitor keywords can capture users in the consideration phase.
8. Local Keywords: Catering to Geographic Relevance
Local keywords are also important for physical businesses. Examples include “restaurants near me” or “digital marketing agency in Los Angeles.” Optimizing for local keywords involves incorporating location-specific terms in your content and metadata, ensuring your business appears in local search results.
9. Trend-Driven Seasonal Keywords: Ride the Seasonal Trends
Seasonal keywords align with specific seasons, events, or trends. Examples include “summer fashion trends” or “holiday gift ideas.” Capitalizing on seasonal keywords requires timely content creation and promotions, allowing you to ride the wave of trending topics and attract users actively seeking seasonal information.
10. Semantic Keywords: Embracing Contextual Relevance
Semantic keywords focus on the context and intent behind user queries. Search engines increasingly prioritize understanding the context of content. For instance, if your main keyword is “apple,” semantic keywords might include “fruit,” “iPhone,” or “orchard.” Incorporating semantic keywords ensures your content aligns with the broader context of user intent.
Strategies for Integrating Keyword Types: A Harmonious Approach
1. Comprehensive Keyword Research
Start your search engine optimization (SEO) journey with keyword research. Utilize tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to identify relevant keywords across various types. Understand user intent and the competitive landscape for each keyword.
2. Create Targeted Landing Pages
Tailor your landing pages to specific keyword types. For instance, create product pages optimized for transactional keywords, blog posts for informational and long-tail keywords, and localized pages for local keywords. This ensures a seamless user experience aligned with their search intent.
3. Optimize Metadata and Content
Infuse your metadata (titles, meta descriptions) and content with strategically chosen keywords. Ensure a natural flow and user-friendly experience, avoiding keyword stuffing. Well-optimized metadata improves click-through rates, and keyword-rich content enhances search engine visibility.
4. Regularly Update and Refresh Content
Keep your content relevant and up-to-date. Google favors fresh content, and regularly updating your pages signals to search engines that your website is actively maintaining its information.
5. Monitor and Adjust
Track your keywords’ performance on a regular basis with analytics tools. Track rankings, organic traffic, and user engagement metrics. Adjust your strategy based on the evolving landscape, user behavior, and algorithm changes.
Crafting a Keyword Symphony for SEO Success
Keywords are the notes that create a harmonious melody. Each type of keyword plays a unique role, contributing to the overall resonance of your online presence. By understanding the nuances of these 10 key types, you’re equipped to orchestrate a keyword symphony that resonates with search engines and captivates your audience.
So, embark on your keyword journey with confidence. Integrate a diverse range of keywords into your SEO strategy, aligning with user intent and industry trends. As you navigate the complexities of SEO, let the strategic use of keywords be your guide, propelling your website to new heights of visibility and success.
